How to choose color agent for nylon?
Colors are divided into two major categories: pigments and dyes, of which pigments are divided into inorganic pigments and organic pigments. Since the characteristics of nylon have special requirements for colorants, today we will mainly look at how to choose colorants for nylon.
1. About nylon
(1) What are the characteristics of nylon?
Nylon has high mechanical strength, high softening point, heat resistance, low friction coefficient, wear resistance, self-lubrication, shock absorption and noise reduction properties; oil resistance, weak acid resistance, alkali resistance and general solvent resistance; electrical insulation Good, self-extinguishing; non-toxic, odorless, good weather resistance; but poor dyeability.
(2) Main applications of nylon
One of the main uses of polyamide is in synthetic fibers. Its most outstanding advantage is that its wear resistance is higher than that of all other fibers. Because polyamide is non-toxic, it can be used as medical sutures.
Because polyamide is safe, lightweight, has excellent mechanical strength, wear resistance and good corrosion resistance, it is increasingly used to replace metals such as copper in machinery, chemical industry, instrumentation, automobiles, etc. Bearings, gears, pump blades and other parts are manufactured in industry.
In industry, nylon is widely used to make cords, industrial fabrics, cables, conveyor belts, tents, fishing nets, etc.
In the defense industry, it is used as the first choice material for parachutes and other military fabrics.
2. Classification and performance comparison of colorants
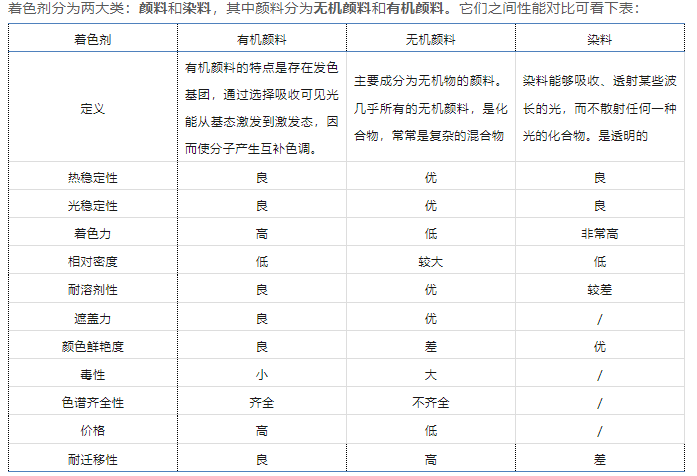
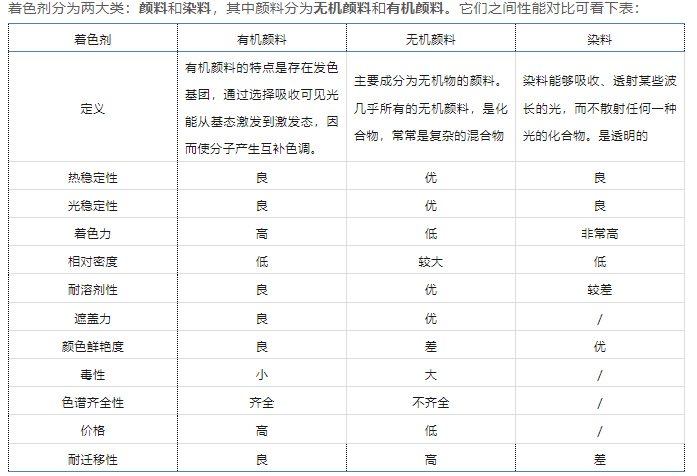
Colors are divided into two major categories: pigments and dyes, of which pigments are divided into inorganic pigments and organic pigments. The performance comparison between them can be seen in the table below:
The characteristic of organic pigments is the presence of chromophoric groups, which excite from the ground state to the excited state by selectively absorbing visible light energy, thus causing the molecules to produce complementary hues.
Pigments whose main components are inorganic substances. Almost all inorganic pigments are compounds, often complex mixtures
Dye is a compound that absorbs and transmits certain wavelengths of light without scattering any kind of light. is transparent
3. What properties do colorants for nylon need to possess?

(1) Heat and light resistance:
So far, many organic pigments, inorganic pigments and solvent dyes can be used for coloring most thermoplastic engineering plastics.
Resin processing temperature and colorant requirements:
As can be seen from the table, the processing temperature of polyamide is very high, and the colorants used need to have high heat resistance. As for organic pigments for plastics, in addition to certain requirements for their thermal stability, It also needs to have good light fastness. Many organic pigments have significant negative effects on the performance of polyamide melts, so there are certain restrictions on the organic pigments used for polyamide coloring.
(2) Chemical stability:
The colorant and the resin should not react chemically or promote the decomposition of the resin. For highly reactive resins such as polyamide resin (PA), its molten state shows reducing properties, which easily causes the colorant to change color. Therefore, there are only a few colorants to choose from.
(3) Migration resistance:
There are three main types of colorant migration:
(1) Solvent extraction, that is, color bleeding in water and organic solvents;
(2) Contact migration, causing contamination of adjacent objects;
(3) When the surface is frosted, the solubility of the colorant in the polymer is greater when heated, and at room temperature, the coloringThe solubility of �� is small.
Generally speaking, the dispersion of inorganic pigments in polymers is heterogeneous and will not cause blooming; while organic pigments are dissolved to varying degrees in polymers and other organic matter and are relatively prone to migration.
(4) Tinting power:
The tinting power determines the amount of colorant used to achieve the target color. Generally speaking, tinting power increases as the colorant particle size decreases. The tinting power of organic pigments is higher than that of inorganic pigments. When color pigments and white pigments are used together, the tinting power can be significantly improved.
(5) Dispersion:
Only when the colorant is evenly dispersed in the form of tiny particles in the polymer can it have a good coloring effect. Pigments contain many aggregated particles, and high shear force must be used to break large aggregates into small aggregates to meet the requirements.
4. How to choose colorants for nylon?
Combined with the characteristics that nylon colorants need to meet and the performance comparison table of several colorants:
Inorganic pigments are superior to organic pigments in terms of light resistance, weather resistance, migration resistance, and chemical resistance. They are generally suitable for plastics, but the color intensity and brightness are much worse. When good color is required, organic pigments are preferred. In addition, inorganic pigments have a high reflection index and are often used in opaque products.
Organic pigments show high coloring strength and brightness compared to inorganic pigments. The processing temperature of PA is high, and the requirements for the heat resistance and stability of the pigment are also high. At the same time, the PA resin shows strong reducing properties when melted, making many organic pigments for plastics unsuitable for use in nylon.
At present, the organic pigments suitable for nylon, especially the light-colored varieties, are still lacking and require in-depth research. Therefore, the only choice for brighter colors is dyes.
Dye, a colorant that can be dissolved in water, oil or organic solvents. Dyes are generally organic compounds. The advantages of dyes are bright colors, eye-catching colors, and complete color spectrum. However, the disadvantages are poor heat resistance, weather resistance, and solvent resistance. They are prone to decomposition and discoloration at plastic processing temperatures or during use at higher temperatures. Although the dye has poor temperature resistance, the color will eventually stabilize after being exposed to high temperatures in nylon, and a certain degree of freshness can still be achieved. In addition, high-temperature resistant dyes are currently being developed to meet demand.
Dye is the main colorant for textiles such as fibers and fabrics. It is rarely used in plastics and is mainly used in optical plastic products to maintain good transparency of transparent plastics.