A summary of polyurethane soft foam formulas
01
Foreword
Polyurethane soft foam series products mainly include block, continuous, sponge, high resilience foam (HR), self-skinning foam, slow rebound foam, microporous foam and semi-rigid energy-absorbing foam, etc. This type of foam still accounts for about 50% of total polyurethane products. A large variety with an increasingly expanding application range, it has been involved in various fields of the national economy: home appliances, automobiles, home decoration, furniture, trains, ships, aerospace and many other fields.
Since the advent of PU soft foam in the 1950s, especially after entering the 21st century, there has been a rapid development in terms of technology, variety and product output. What stands out are:
Environmentally friendly PU soft foam, that is, green polyurethane products; low VOC value PU soft foam; low atomization PU soft foam; full water PU soft foam; full MDI series soft foam; flame retardant, low smoke, full MDI series foam; reactive type New types of additives such as high molecular weight catalysts, stabilizers, flame retardants and antioxidants; polyols with low unsaturation and low monool content; ultra-low density PU soft foam with excellent physical properties; low resonance frequency and low transmissibility PU soft foam; polycarbonate diol, polyε-caprolactone polyol, polybutadiene diol, polytetrahydrofuran and other special polyols; liquid CO2 foaming technology, negative pressure foaming technology, etc. ·
In short, the emergence of new varieties and new technologies has promoted the further development of PU soft foam.
02
Foaming principle
If you want to synthesize an ideal PU soft foam that meets the requirements, you must understand the chemical reaction principle of the foam system in order to select the appropriate primary and auxiliary raw materials and manufacturing process. The development of the polyurethane industry to this day is no longer in the imitation stage. Instead, it can be achieved through raw material structure and synthesis technology based on the performance requirements of the final product. For this reason, it is crucial to master the foaming principle.
Polyurethane foam participates in chemical changes during the synthesis process, and the changing factors that affect the structural properties of the foam are complex, which not only involves the chemical reaction between isocyanate, polyether (ester) alcohol, and water, but also involves the colloidal chemistry of foaming. Its chemical reactions include processes such as chain extension, foaming and cross-linking. It also affects the structure, functionality, molecular weight, etc. of the substances participating in the reaction.
The total reaction of general polyurethane foam synthesis can be expressed by the following formula:
However, the actual situation is more complicated. The important reactions are summarized as follows:
01 Chain extension
The chain extension of polyfunctional isocyanates and polyether (ester) alcohols, especially difunctional compounds, is carried out as follows: Picture
In the foaming system, the amount of isocyanate is generally greater than the active hydrogen-containing compound, that is, the reaction index is greater than 1, usually 1.05, so the end of the chain extension product during the foaming process should be an isocyanate group.
Pictures
The chain extension reaction is the main reaction of PU foam and is the key to physical properties: mechanical strength, elongation, elasticity, etc.
02Foaming reaction
Foaming is very important in the preparation of soft foam, especially when synthesizing low-density products. There are generally two types of foaming effects: the use of reaction heat to vaporize low-boiling hydrocarbon compounds, such as HCFC-141b, HFC-134a, HFC-365mfc, cyclopentane, etc. to achieve foaming purposes; the other is the use of the interaction between water and isocyanate Chemical reaction produces a large amount of CO2 gas for foaming: In the absence of a catalyst, the reaction rate between water and isocyanate is slow.
The reaction rate between amines and isocyanates is quite fast. Therefore, when water is used as a foaming agent, it brings a large number of rigid segments and highly polar urea compounds, which affect the feel, resilience and heat resistance of foam products. To produce foam with excellent physical properties and low density, the molecular weight of the polyether (ester) alcohol and the softness of the main chain must be increased.
03Gel effect
The gel reaction is also called cross-linking and curing reaction. The gel effect is very important in the foaming process. If the gel effect is too early or too late, the quality of the foam products will decrease or become waste products. The ideal state is for the chain extension, foaming reaction and gel reaction to reach a balance, otherwise the foam density will be too high or the foam will collapse.
There are three gelling effects during the foaming process:
01 Gel of multifunctional compounds
Generally, the reaction of compounds with three or more functionalities can form body-structured compounds. When we produce polyurethane flexible foam, we use polyether polyols with more than three functionalities. Recently, it has been developed that polyisocyanates with fn≥2.5 are also incorporated into full MDI systems to improve the load-bearing capacity of low-density foam. These are the basis for forming a three-phase cross-linked structure:
It is worth noting that the molecular weight between cross-linking points directly reflects the cross-linking density of the foam. That is to say, the cross-linking density is high, the product has high hardness and good mechanical strength, but the foam has poor softness, low resilience and low elongation.
The molecular weight (Mc) between the cross-linking points of soft foam is 2000-2500, and that of semi-hard foam is between 700-2500.
02 Formation of biuret When water is used as the foaming agent, urea bond compounds are produced accordingly. The more water, the more urea bonds. They will further react with excess isocyanate at high temperatures to form biuret bonds with a three-phase structure. Compounds:
3). Formation of allophanate
Another type of cross-linking reaction is that hydrogen on the urethane main chain further reacts with excess isocyanate at high temperatures to form an allophanate bond with a three-phase structure:
The formation of biuret compounds and allophanate compounds is not ideal for foaming systems because these two compounds have poor thermal stability and decompose at high temperatures. So people are livingIt is crucial to control the temperature and isocyanate index during the process.
03
Chemical calculations
Polyurethane synthetic material is a polymer synthetic material that can synthesize polymer products from raw materials in one step. In other words, the physical properties of the product can be artificially adjusted directly by changing raw material specifications and composition ratios. Therefore, how to correctly apply the principles of polymer synthesis and establish simple calculation formulas is very important to improve the quality of polyurethane products
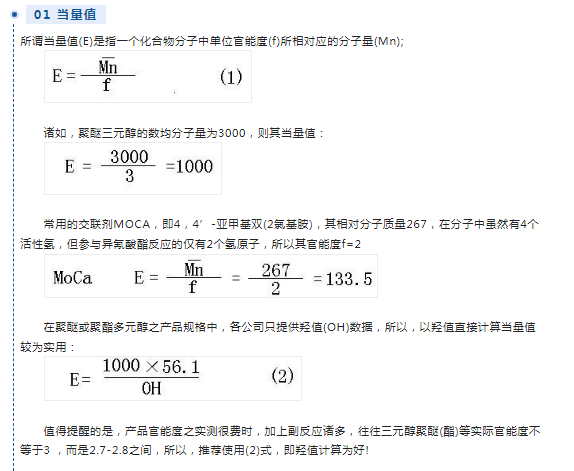
01 equivalent value
The so-called equivalent value (E) refers to the molecular weight (Mn) corresponding to the unit functionality (f) in a compound molecule;
For example, if the number average molecular weight of polyether triol is 3000, then its equivalent value is:
The commonly used cross-linking agent MOCA, namely 4,4′-methylenebis(2chloroamine), has a relative molecular mass of 267. Although there are 4 active hydrogens in the molecule, only 2 hydrogens participate in the isocyanate reaction. Atom, so its functionality is f=2
In the product specifications of polyether or polyester polyols, each company only provides hydroxyl value (OH) data, so it is more practical to directly calculate the equivalent value based on the hydroxyl value:
It is worth reminding that the actual measurement of product functionality is time-consuming, and there are many side reactions. Often the actual functionality of triol polyether (ester) and other products is not equal to 3, but between 2.7-2.8. Therefore, it is recommended to use (2 ) formula, that is, the hydroxyl value is calculated!
02 Requirement of isocyanate
All active hydrogen compounds can react with isocyanate. According to the principle of equivalent reaction, it is common in PU synthesis to accurately calculate the amount of isocyanate consumed by each component in the formula: